Accidental Yarnover

A loop (yarnover) that gets put onto your needle accidentally. A yarnover makes a lacy hole in your knitting. If this is not wanted, make sure to catch it and remove it as soon as possible.
How to Fix Mistakes in Ribbing
Found in: Mistakes and Errors
American/English-Style Knitting

Knitting with the working yarn in your right hand.
Found in: Kinds of Knitting
Aran

A medium-thick weight of yarn. Aran-weight yarn knits up at a gauge of 4 sts/in. (16 sts/4 cm). Aran is thinner than Chunky and thicker than Worsted.
Found in: Yarn Weights
Back Loop

The leg of the stitch that is behind the needle. In knitting instructions the back loop is referred to in the abbreviation tbl (through the back loop).
Whichever leg is behind the needle is referred to as the back loop.
Found in: Stitch Terms
Beginning of Round

The place where you started the round. Usually your tail yarn can be found here.
Found in: Pattern Terms
Bind Off

Secure your stitches and take them off the needles after you have finished knitting.
Found in: Basic Stitches
Blocking

The practice of soaking your knitting in warm water and laying it flat to dry after you finish knitting it. Blocking makes edges straight, stitches even, and fabric lay flat.
Found in: Techniques
Bobbin

A length of (leftover) yarn coiled into a self-contained figure-8. In a center-pull bobbin, you pull the working yarn from the center.
Found in: Yarn Put-Ups
Cast On

Put stitches onto your needle so you can begin knitting.
Found in: Basic Stitches
Center-Pull Ball

The form which a ball of yarn has when it is wound to enable you to pull the working yarn from the center.
Found in: Yarn Put-Ups
Chunky

A bulky thickness of yarn. Chunky-weight yarn (also called Bulky) knits up at a gauge of 3.5 sts/in. (14 sts/4 cm). Chunky is thinner than Super-Bulky and thicker than Aran.
Found in: Yarn Weights
Circs/Circulars

Found in: Abbreviations, Needles
Circular Needles

Two knitting needle tips connected by a flexible cable. Circular needles are used for big, flat projects and knitting in the round.
Found in: Needles
Colorway

Any individual color-combination of a line of multicolor yarns.
Found in: Yarn Terms
Colorwork

Knitting with multiple colors to make a design.
Found in: Kinds of Knitting
Continental Knitting

Knitting with the working yarn in your left hand.
Found in: Kinds of Knitting
Contrasting Color

The color of yarn that is not the main color. Often this is a secondary accent color, but not always. See main color, above.
Found in: Pattern Terms
Decrease

Combine two or more stitches into one so that your project gets narrower.
Found in: Pattern Terms
DK

A medium weight of yarn – just thinner than Worsted.
Gauge on size US 6 needles: 5.5 sts/in.
Found in: Yarn Weights
Double-Pointed Needles

Short, double-ended needles used for knitting in the round. Often referred to as DPNs.
Found in: Needles
DPN(s)

Found in: Abbreviations, Needles
Dye Lot

The batch that a ball of yarn was dyed in. Yarns of the same color and the same dye lot will look more similar to each other than yarns of the same color but of different dye lots.
Found in: Yarn Terms
Felting

A technique in which you knit something out of pure wool and then wash it in hot, soapy water. The garment shrinks and gets thicker as the stitches fuse together. If you have ever shrunk a wool sweater in the washing machine, you’ve done felting.
Found in: Techniques
Fingering

A fine thickness of yarn. Fingering-weight yarn (also called Sock) knits up at a gauge of 7 sts/in (28 sts/4 cm). Fingering is thinner than Sport and thicker than Lace.
Found in: Yarn Weights
Flat Knitting

Knitting back and forth on straight needles to make a piece of knitting that is flat. Examples of things that are knit flat are scarves, dishcloths, and baby blankets. The opposite of flat knitting is round knitting (knitting in the round).
Found in: Kinds of Knitting
Frogging

Unraveling your knitting (usually entirely). Frogging gets its name from what you do when you unravel: “rip-it, rip-it.”
Found in: Mistakes and Errors
Garter Stitch

The reversible fabric created when you knit every row. Garter stitch is characterized by its horizontal ridges.
Found in: Basic Stitches
Gauge

“How big your stitches are and how big they should be to make your project come out the right size.
Gauge is measured in stitches per inch or as the number of stitches in 4 in./10 cm.”
Found in: Pattern Terms
Gauge Swatch

A small sample of knitting made especially in order to check your gauge.
Found in: Techniques
Getting Gauge

Achieving the gauge called for in your pattern. To do so, make a swatch and check your gauge. If it does not match the gauge specified in your pattern, adjust your needle size up or down and knit a new swatch. Repeat this process until your gauge matches the target gauge.
Found in: Techniques
Grabby

A characteristic of some knitting needles. Grabby means having a coating or finish that helps yarn not to slide on the needle.
Found in: Needle Terminology
Hank

The shape that yarn is twisted into to make it compact for dyeing and displaying. Hanks must be wound into balls before you can knit with them. Most people incorrectly use the word “skein” for yarn in this shape. I recommend you do the same (unless you’re writing a blog post or something where people will call you out).
Found in: Yarn Put-Ups
Heathered

A style of yarn dyeing that incorporates tiny flecks or section of lighter shades into the main color of the yarn. Heather-dyed yarns have a soft, weathered look, like stonewashed denim.
Found in: Kinds of Yarn Color
Highly Variegated

Multicolor yarns that change color every few stitches. The frequent color changes break up the different colors and distribute them more or less evenly throughout the finished piece. Misti Alpaca is one company famous for making highly variegated yarn.
Found in: Kinds of Yarn Color
In Pattern

According to the same stitch pattern you’ve been following.
Found in: Pattern Terms
In the Round

Worked on double-pointed or circular needles, forming a tube.
Found in: Kinds of Knitting
Increase

Add more stitches to your needle to make your knitted project wider.
Found in: Pattern Terms
Kettle-Dyed

A style of yarn dyeing
Found in: Kinds of Yarn Color
Knit Up (Verb)

The way in which a yarn turns into knitted fabric, or the characteristic of the yarn when it is knitted. How the yarn looks and feels when it has been knitted into stitches.
For example:
“This yarn knits up really soft” = “This yarn feels really soft when it’s in a knitted garment.”
“This yarn knits up really fast” = “This yarn is so thick that if you knit a project with it you will finish really quickly.”
Found in: Lingo
Knitting Flat

See Flat Knitting
Found in: Kinds of Knitting
Knitting Pattern

All the instructions required in order to knit a project.
Knitting patterns are written using abbreviations.
The crucial elements of a knitting pattern are
1) size and finished measurements
2) gauge
3) materials
4) knitting instructions, and
5) finishing instructions.
Found in: Other
Knitwise

With the needle going into the stitch from front to back, as if to knit.
Contrast with Purlwise.
Found in: Stitch Terms
Lace

A very fine weight of yarn. Use size 0-9 needles to create cobweb-like lace patterns.
Gauge of laceweight yarn on size US 0 needles is 9 sts/in.
Found in: Yarn Weights
Leg

One half of a loop of yarn on the needle. The front leg is the half closest to the tip of the needle. The back leg is the half furthest from the needle tip.
Contrast this with back loop.
Found in: Stitch Terms
Local Yarn Store

A brick-and-mortar store that specializes in selling yarn for knitting, crocheting and other crafts.
Ravelry yarn store locator: https://www.ravelry.com/shops/search
Found in: Lingo
LYS

See Local Yarn Store
Found in: Abbreviations
Magic Loop

A clever way to knit in the round using one long circular needle. Magic Loop refers to the technique itself, not any specific piece of equipment.
Found in: Techniques
Main Color

The color of yarn that you or the pattern designer has designated as the main color. This color doesn’t necessarily have to be more dominant in the pattern than any other color. It’s just important to keep straight which one is which, usually by writing it down.
Found in: Pattern Terms
Mosaic Knitting

A way of using slipped stitches to create a color design. The trick is that, even though you are using two or more colors, you knit with only one color at at time. This makes mosaic knitting an ideal colorwork technique for beginners.
Found in: Kinds of Knitting
Multiple (Noun)

The number of stitches in a repeating section of a stitch pattern. Multiples are used to calculate various options for cast-on numbers, so that you can knit a stitch pattern in more than one width.
Found in: Pattern Terms
Pull From the Center

Work from the yarn that is coming out the of the middle of the ball. Pulling from the center means the ball of yarn won’t roll around.
Found in: Yarn Terms
Pull From the Outside

Work from the yarn that is coming from the outside of the skein. Pulling from the outside may cause the ball of yarn to roll around.
Found in: Yarn Terms
Purlwise

With the needle going into the stitch from back to front, as if to purl.
Contrast with knitwise.
Found in: Stitch Terms
Read Your Work

Count your stitches and rows and differentiate between knit and purl stitches. Read your work to know what you’ve just done, where you are in the pattern, and what you need to do next.
Found in: Techniques
Reverse Stockinette Stitch

The fabric created when you purl on the right side of the fabric and knit on the wrong side. In knitting patterns, Reverse Stockinette stitch is abbreviated as “Reverse Stockinette st” and “Rev St st.”
The wrong side of Stockinette stitch is called Reverse Stockinette stitch. It is created by purling on the right side and knitting on the wrong side. If you’re not knitting it as part of a pattern, you can also just knit in regular Stockinette stitch and then turn the fabric over.
To do Reverse Stockinette Stitch
Row 1 (RS) and all RS rows: P.
Row 2 and all WS rows: K.
Found in: Basic Stitches
Ribbing

Alternating knit and purl stitches to form a stretchy, reversible fabric. In ribbing, knit and purl stitches stack up in columns. Ribbing can be made of any combination of knits and purls, as long as they stack up. Examples are 1×1 rib, 2×3 rib, 2×4 rib, etc.
Found in: Basic Stitches
Right Side

The side of your knitting intended to be visible when the project is worn.
Found in: Pattern Terms
Round (Noun)

The circular row of stitches formed when you work around your stitches one time. Applies to knitting in the round.
Found in: Pattern Terms
Round Knitting

Found in: Kinds of Knitting
Self-Striping

Yarn dyed so that stripes of color form as you knit.
Found in: Kinds of Yarn Color
Semi-Solid

The yarn is dyed one main color, with visible variations in intensity of color.
Found in: Kinds of Yarn Color
Short-Tail Cast-On

A cast-on that only uses one strand of yarn (the working yarn) to create stitches. The tail is not used in a short-tail cast-on and can therefore be cut short.
Found in: Techniques
Skein

A ball of yarn. The term “skein” is often used erroneously to mean “hank,” while “ball” is a more common word for a skein.
Found in: Yarn Put-Ups
Sport

A medium-fine weight of yarn. Between fingering-weight and DK weight.
Gauge of sport-weight yarn on size US 4 needles: 6 sts/in.
Found in: Yarn Weights
Stash

A knitter’s accumulated yarn supply. On Ravelry.com, your stash is a digital record of your real-life stash.
Found in: Lingo
Stitch

A stitch is
- Any loop of yarn that is on your needle or
- Any loop of yarn that was on your needle and is now part of the knitted fabric.
In knitting patterns, “stitch” is abbreviated as “st” and “stitches” is abbreviated as “sts.”
Found in: Stitch Terms
Stockinette Stitch

The fabric created when you knit on the right side of the fabric and purl on the wrong side. In knitting patterns, Stockinette stitch is abbreviated as “Stockinette st” and “St st.” Stockinette stitch is also called Stocking stitch.
Found in: Basic Stitches
Straight Needles

Straight knitting needles are used to knit flat projects back-and-forth. They come in lengths from about 9-14″ (sort of like magic wands).
They are made from materials like birch, bamboo, aluminum, and exotic woods. My favorites are Signature Needles Stiletto tip, and Lantern Moon wooden needles.
Found in: Needles
Super-Bulky

A very bulky weight of yarn.
Super-bulky yarn knits up on size US 13-15 needles at a gauge of 2.5 sts/in.
Found in: Yarn Weights
Swatch

A small sample of knitting. Knitters make swatches in order to practice new techniques or test out stitch patterns. Swatches are also crucial for checking gauge.
Found in: Techniques
Tail

In knitting, the word “tail” can refer to two things.
1) A tail is any end of yarn sticking out after you finish a project. Tails must be woven in to prevent unraveling. Whenever cutting a piece of yarn, always leave at least a 6-in. (15 cm) tail so that you can weave it in later. This type of tail is also called an “end.”
2) In doing any kind of long-tail cast-on, the tail is the strand of yarn coming from your needle that is not the working yarn.
Found in: Yarn Terms
Tension (Verb and Noun)
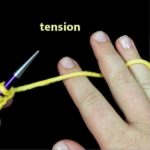
To tension your yarn is to hold it comfortably in your fingers so that you can knit with it. The tension is the tightness or looseness of your stitches in consequence of how you are holding the yarn.
Found in: Other
Tink

To “un-knit,” i.e., undo your knitting stitch by stitch. The work “tink” gets its name from “knit” spelled backwards.
Found in: Lingo, Mistakes and Errors
Turn Work

To flip your knitting so that the other side is facing you. On flat knitting, you have to turn your work after you finish every row. In pattern instructions, “turn your work” is shortened to “turn.”
Found in: Pattern Terms
Variegated

Multicolor yarn dyed to create splotches or areas of color in the finished piece.
Found in: Kinds of Yarn Color
Weave In

Secure and hide your yarn ends by weaving them through the stitches on the back of your work.
Found in: Techniques
Weight

The official thickness category a yarn falls into. E.g. worsted weight and bulky weight are two standard thicknesses (weights) of yarn. NB: A yarn’s weight in this sense isn’t directly related to its actual physical weight in ounces or grams. That has more to do with the density of the yarn.
Found in: Yarn Terms
Work Even

Work the stitches exactly as they are: knit a knit stitch, purl a purl stitch, and slip a slipped stitch.
Found in: Pattern Terms
Working Yarn

The yarn you are knitting with, i.e., the strand of yarn coming from the ball.
Found in: Yarn Terms
Worsted

A medium thickness of yarn, worsted is thinner than Aran and thicker than DK.
Worsted-weight yarn knits up at a gauge of 5 sts/in. (20 sts/4 cm) on size US 7 needles.
Found in: Yarn Weights
Wrong Side

The side of your knitting intended to be hidden when the project is worn
Found in: Pattern Terms
Yardage

Yarn length. This can refer to
1) How many yards of yarn a ball of yarn contains or
2) The length of yarn required to knit a project.
Found in: Pattern Terms
Wrap

The cape-like yarnover stitch that accompanies slipped stitches in brioche knitting.
Found in: Brioche
Yarnover

A wrap of yarn that creates a new stitch on the needle. A yarnover is a type of increase that is easy for beginners. It creates a lacy hole.
Found in: Basic Stitches

